Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Capitellum
Osteochondritis dissecans of the capitellum is a condition affecting the bone and cartilage of the capitellum (part of the outer side of the elbow). This disorder primarily occurs in children and adolescents during their growth phase and is often caused by repetitive stress on the elbow joint from sports activities such as baseball pitching and tennis serving. It is a type of osteochondritis dissecans, and as the condition progresses, fragments of cartilage or bone may become loose and float within the joint, forming joint mice.
Mechanism of Occurrence
The outer side of the elbow joint experiences concentrated compressive and shear forces from repetitive pitching and swinging motions. Persistent stress reduces blood flow to the bone and cartilage of the capitellum, making the tissue more susceptible to necrosis. As a result, the bone and cartilage may separate and detach.
Main Causes
- Repetitive Sports Movements:
・Repetitive elbow motions such as baseball pitching and tennis swinging. - Excessive Load:
・Prolonged practice, games, or exceeding pitching limits. - Growth-Specific Bone Weakness:
・The growth plates are not fully developed, resulting in lower durability. - Poor Form:
・Inefficient pitching or swinging motions that place excessive stress on the elbow.
Symptoms
- Elbow Pain:
・Initially mild pain after sports activities, progressing to pain at rest as the condition worsens. - Limited Range of Motion:
・Difficulty fully extending or bending the elbow. - Swelling and Tenderness:
・Mild swelling and pain when pressing on the outer part of the elbow. - Clicking or Locking Sensation:
・As joint mice form, there may be a clicking or locking sensation when moving the elbow. - Muscle Weakness:
・Reduced strength in the arm and hand due to pain.
Diagnosis
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
・Confirm the location and history of pain, and sports participation history.
・Evaluate the range of motion and tenderness of the outer elbow. - Imaging Tests:
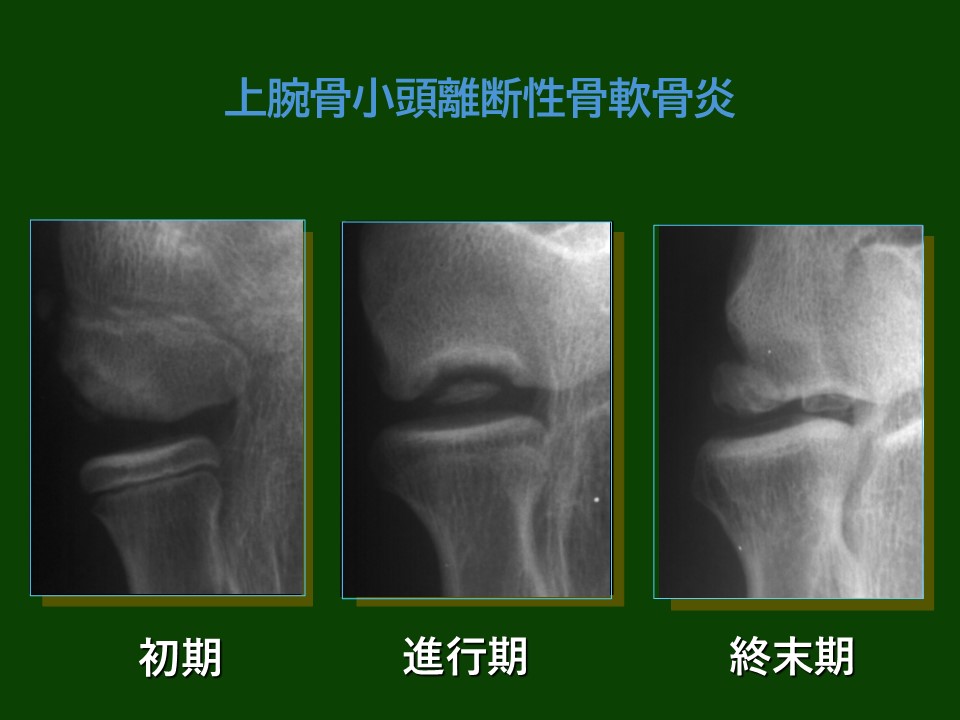
・X-ray:Confirm bone shape and separation.
・MRI: Detailed assessment of cartilage and bone condition, and blood flow issues.
・CT Scan:Detailed structure of the joint and location of joint mice.
・Ultrasound:Sometimes used for dynamic evaluation.
Treatment
Conservative Therapy (Mild to Moderate)
- Cessation of Sports Activities:
・Temporarily stop sports to avoid further stress. - Use of Orthotics:
・Ensure elbow stability with elbow supports or splints. - Icing:
・Reduce pain and inflammation through cooling. - Rehabilitation:
・Exercise therapy aimed at strengthening muscles and restoring range of motion. - Periodic Monitoring:
・Regular imaging tests to monitor progress.
Surgical Therapy (Severe or Advanced Cases)
[Bone and Cartilage Repair]
・Fixation of the detached area to its original position.
[Removal of Joint Mice]
・Removal of loose fragments within the joint.
[Bone Grafting and Cartilage Repair Surgery]
・Surgery to supplement bone and cartilage if necrosis is extensive.
Recovery Period
- Mild: Return to sports in a few months.
- Moderate: Requires six months of rest and rehabilitation.
- Severe: May take over a year for complete recovery post-surgery.
Prevention
- Adherence to Pitching Limits:
・Follow pitch count and rest days. - Learning Proper Form:
・Learn techniques that do not place excessive stress on the elbow and shoulder. - Strength Training:
・Strengthen the muscles of the elbow, shoulder, and core for stability. - Stretching and Flexibility Improvement:
・Perform thorough warm-up and cool-down before and after pitching or practice. - Growth Period Management:
・Develop training plans considering the development status of bones and joints in children.
Note: Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial. If left untreated, it can lead to joint deformities and functional impairments. If elbow pain persists, it is important to consult an orthopedic specialist promptly.
Outpatient Reception & Consultation Hours
| Business Hours | 月 | 火 | 水 | 木 | 金 | 土 | 日 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13:00~17:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
| 18:00~20:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
【Closed Days】 Wednesday, Saturday, and Public Holidays.
※translates to "Reception ends 30 minutes before the end of consultation hours."
