Impingement Syndrome
Main Characteristics
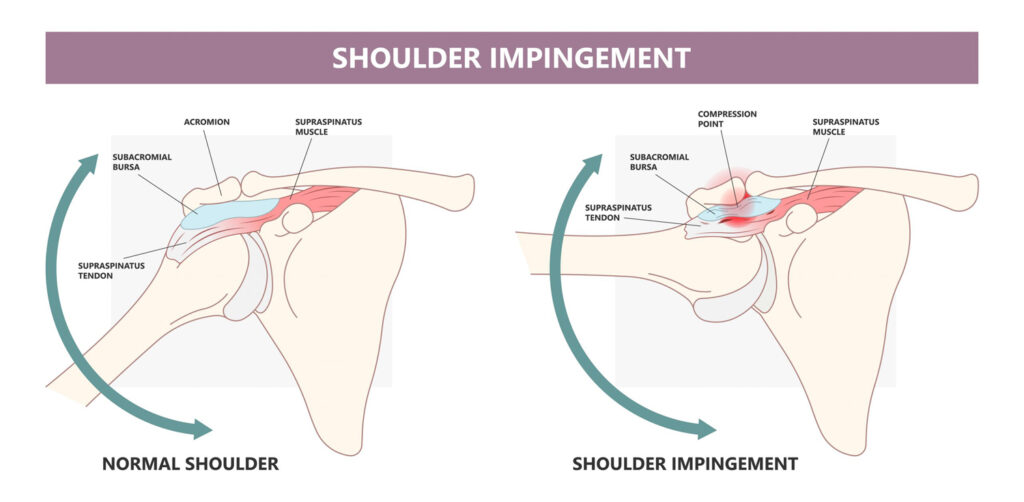
Impingement syndrome is a condition where the muscles and tissues in the shoulder get compressed between the head of the upper arm bone and the underside of the shoulder blade (acromion) during movement. This can lead to pain and restricted movement in the shoulder.
Causes
Thickening of tendons (rotator cuff) can lead to compression, shoulder instability, and external trauma or overuse, especially in athletes performing overhead movements.
Symptoms
・Sharp pain on the outside or front of the shoulder, especially when lifting the arm above 90 degrees
・Restricted range of motion
・Nighttime pain that interrupts sleep
Diagnosis
・Medical interviews to check symptoms and onset
・Physical exams to assess shoulder mobility and pain
・Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to examine the structure and condition of the muscles and tendons
Treatment
・Rest to avoid painful movements
・Cold therapy to reduce swelling and inflammation
・Physical therapy to restore shoulder mobility and strength
・Medication such as NSAIDs
・Surgery if other treatments are ineffective or if severe impingement is confirmed
Prevention
・Stretching and strengthening exercises for shoulder muscles
・Learning proper techniques for sports and daily activities
Summary
Impingement syndrome is a condition where tendons in the shoulder get compressed, causing pain, and requires proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention and rehabilitation are crucial for recovering shoulder function and returning to daily activities.
Differences Between Impingement Syndrome and Rotator Cuff Tears
Impingement syndrome and rotator cuff tears both cause shoulder pain and limited range of motion, but they stem from different causes and conditions.
Impingement Syndrome
Impingement syndrome occurs when the space between the acromion (a part of the shoulder blade) and the humerus (upper arm bone) narrows during shoulder movement, compressing the rotator cuff and subacromial bursa, leading to inflammation.
・Causes: Repetitive overhead activities or sports, shoulder overuse, muscle weakness around the shoulder, poor posture.
・Main symptoms: Pain when lifting the arm, especially above shoulder level, night pain, and restricted shoulder movement.
・Treatment: Rest, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy for stretching and strengthening shoulder muscles, posture correction, and sometimes surgery to reshape the acromion.
Rotator Cuff Tears
Rotator cuff tears involve damage to the rotator cuff tendons (particularly the supraspinatus tendon), which help stabilize and move the shoulder. When torn, muscle strength is lost, severely impairing shoulder function.
・Causes: Age-related wear and tear, acute injuries from falls or impacts, and chronic impingement syndrome leading to tendon damage.
・Main symptoms: Pain (especially at night), limited arm movement, and weakness in the affected shoulder.
・Treatment: Mild tears might be managed with rehabilitation and pain relief, but full tears often require surgery.
Summary of Key Differences
| Feature | Impingement Syndrome | Rotator Cuff Tears |
|---|---|---|
| Causes | Inflammation due to compression and friction of shoulder tendons and bursa | Partial or complete tears of the rotator cuff tendons |
| Pain Location | Shoulder joint, especially when lifting the arm or at night | Pain throughout the shoulder, difficulty moving the arm |
| Treatment | Rest,rehabilitation, sometimes surgery | Rehabilitation, pain relief, and surgery for tears |
Outpatient Reception & Consultation Hours
| Business Hours | 月 | 火 | 水 | 木 | 金 | 土 | 日 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13:00~17:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
| 18:00~20:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
【Closed Days】 Wednesday, Saturday, and Public Holidays.
※translates to "Reception ends 30 minutes before the end of consultation hours."
