Medial Epicondyle Apophyseal Avulsion
Medial epicondyle apophyseal avulsion is a common sports injury in growing children and adolescents, occurring in the medial epicondyle (part of the humerus) of the elbow joint. It is mainly caused by the overloading of repetitive throwing motions in sports such as baseball and tennis. This condition is also known as "Little Leaguer's Elbow."
Mechanism of Occurrence
The medial epicondyle is the attachment site for the medial collateral ligament, which stabilizes the elbow, and the flexor muscles of the wrist. During growth, the apophysis (cartilage area called apophyseal plate) is still ossifying, making it susceptible to avulsion or separation due to excessive traction from repetitive throwing motions.
Main Causes
- Repeated Stress:
・Pitching in baseball.
・Overhead sports like tennis and volleyball. - Sudden Force:
・Excessive load over a short period (sudden increase in game or practice volume). - Improper Form:
・Poor pitching or swinging form placing undue stress on the elbow. - Growth-Specific Bone Structure:
・The immature apophysis during growth has low durability.
Symptoms
- Pain:
・Sharp or dull pain on the inside of the elbow.
・Increased pain after pitching or sports activities. - Swelling:
・Mild to moderate swelling on the inside of the elbow. - Decreased Grip Strength:
・Weakened strength in the hand and arm due to elbow pain. - Limited Range of Motion:
・Difficulty fully bending or extending the elbow. - Chronicity:
・Persistent pain and deformity if left untreated.
Diagnosis
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
・Assess the location and circumstances of the pain, and sports history.
・Evaluate tenderness and swelling around the medial epicondyle. - Imaging Tests:
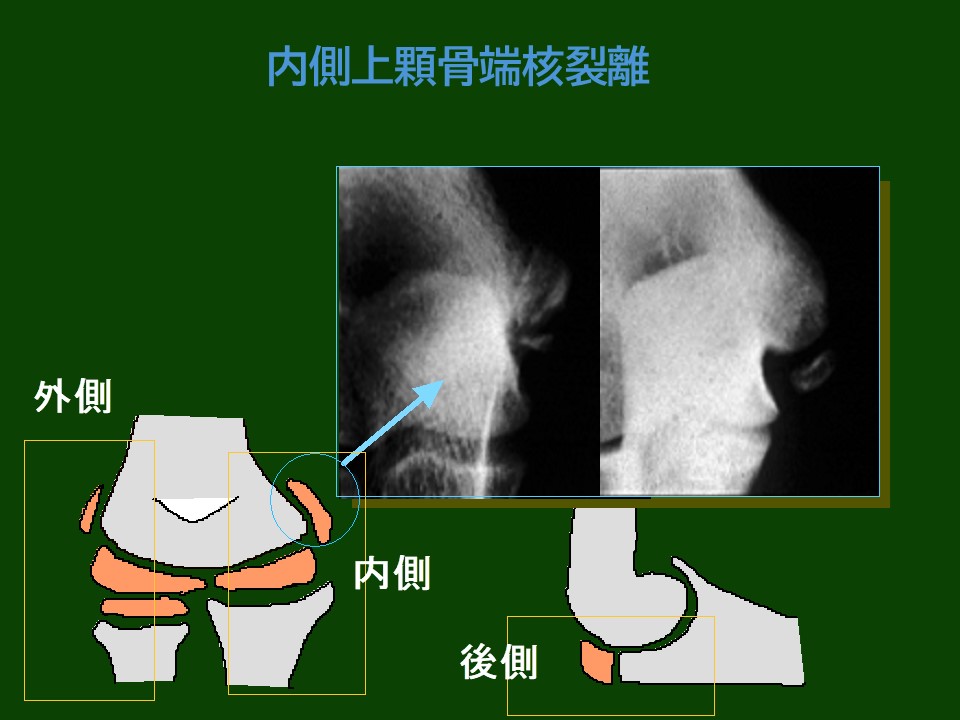
・X-ray:
-Confirmation of apophyseal avulsion or separation.
-Enlargement or deformity of the apophyseal plate may be observed.
・MRI:
-Evaluation of soft tissue and ligament damage.
・Ultrasound:
-Dynamic evaluation or detailed confirmation of avulsion.
Treatment
Conservative Therapy (Mild to Moderate)
- Rest:
・Cease sports activities and avoid stress on the elbow. - Icing:
・Apply cold to reduce pain and inflammation. - Use of Orthotics:
・Immobilize the elbow with splints or elbow supports. - Rehabilitation:
・Programs to restore flexibility and strengthen the elbow and shoulder. - Pitching Restrictions:
・Manage pitch count and improve throwing form.
Surgical Therapy (Severe or Ineffective Conservative Therapy)
・Apophyseal Repair:
-Surgical fixation if the bone fragment is significantly avulsed.
・Ligament Reconstruction:
-Reconstruction surgery if the medial collateral ligament is severely damaged.
Recovery Period
・Mild: Return to sports in several weeks to about 1 month.
・Moderate: Rehabilitation required for 2 to 3 months.
・Severe: Complete recovery may take over 6 months post-surgery.
Prevention
- Proper Form:
・Master correct pitching and swinging techniques. - Load Management:
・Appropriately manage pitch count and training volume. - Strength Training:
・Strengthen muscles around the elbow and shoulder. - Improve Flexibility:
・Ensure thorough warm-up and cool-down routines. - Ensure Rest:
・Allocate appropriate rest days to prevent fatigue accumulation.
Note: Elbow injuries during growth periods can lead to long-term issues if left untreated, so it is essential to seek specialist consultation if pain persists.
Outpatient Reception & Consultation Hours
| Business Hours | 月 | 火 | 水 | 木 | 金 | 土 | 日 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13:00~17:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
| 18:00~20:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
【Closed Days】 Wednesday, Saturday, and Public Holidays.
※translates to "Reception ends 30 minutes before the end of consultation hours."
