Olecranon Stress Fracture
An olecranon stress fracture is a type of fracture that occurs in the olecranon, the bony protrusion at the back of the elbow joint, due to repetitive stress. This condition is commonly seen in sports that involve repeated extension of the elbow, such as pitching in baseball and gymnastics. This fracture progresses from micro-damage caused by fatigue, eventually leading to a complete crack or fracture.
Mechanism of Occurrence
- Repetitive Stress:
・Actions such as pitching or gymnastics that repeatedly extend the elbow put stress on the olecranon. - Incomplete Bone Remodeling:
・Repeated stress causes micro-damage, but the bone is re-stressed before it can fully heal. - Muscle Pulling Action:
・The triceps brachii, which attaches to the olecranon, exerts strong contractions that pull on the bone, causing stress fractures.
Main Causes
- Excessive Sports Activities:
・Common in pitchers in baseball and softball, gymnasts, and volleyball spikers. - Overload:
・Sudden increases in training volume or playing with improper form. - Bone Weakness During Growth:
・Growing children and adolescents have immature bones that are more susceptible to stress fractures. - Lack of Rest:
・Continuing training without adequate recovery periods. - Decreased Bone Density:
・Nutritional deficiencies and osteoporosis are also risk factors.
Symptoms
- Pain at the Back of the Elbow:
・Initially mild pain after sports, progressing to persistent pain. - Swelling and Tenderness:
・Swelling and pain upon touching the olecranon area. - Limited Range of Motion of the Elbow Joint:
・Difficulty fully extending or bending the elbow. - Weakness in the Elbow:
・Reduced strength in activities using the triceps, such as push-ups and pitching. - Clicking or Discomfort:
・A sense of bone instability may be felt.
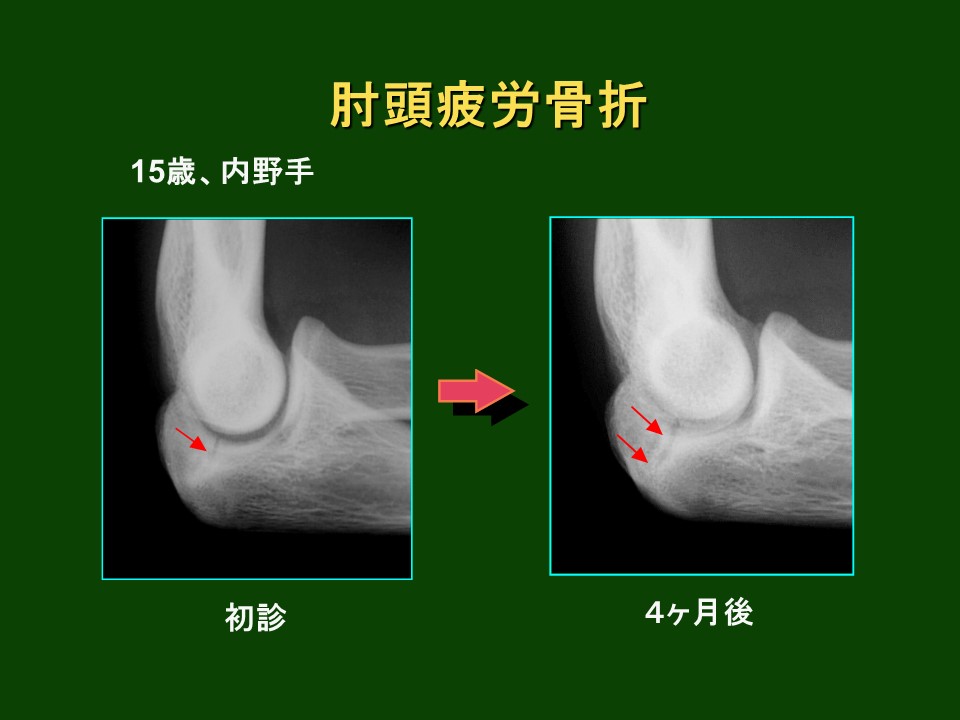
Diagnosis
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
・Confirm the location of pain, sports history, and changes in training volume. - Imaging Tests:
・X-ray: Confirm stress fracture lines and bone deformities.
・MRI: Detailed assessment of bone marrow edema and the progression of the fracture.
・CT Scan: Confirm complex fracture lines and the condition of bone fragments.
・Ultrasound: Assess the impact on soft tissues.
Treatment
Conservative Therapy (Mild to Moderate Fractures)
- Cessation of Sports Activities:
・Suspend sports until symptoms improve. - Use of Orthotics:
・Use casts or splints to stabilize the elbow. - Icing and Anti-inflammatory Drugs:
・Reduce pain and swelling. - Rehabilitation:
・Focus on strength recovery and restoring range of motion after bone healing. - Nutritional Management:
・Increase intake of calcium and vitamin D to promote bone healing.
Surgical Therapy (Severe or Advanced Cases)
- Bone Fixation Surgery:
・Fix the fracture site with screws or plates. - Bone Grafting Surgery:
・Bone grafting from other areas if there is a bone deficiency.
Recovery Period
- Mild Cases: Recovery in 6 to 12 weeks.
- Moderate Cases: Rehabilitation required for 3 to 6 months.
- Post-Surgery: Generally takes 6 to 12 months for a return to sports.
Prevention
- Proper Management of Training Volume:
・Avoid excessive training volumes. - Correction of Form:
・Learn proper movements that minimize stress. - Warm-Up and Stretching:
・Enhance muscle flexibility. - Nutritional Supplementation:
・Ensure adequate intake of nutrients that strengthen bones. - Ensuring Rest:
・Take sufficient rest for bone recovery.
Note: If left untreated, olecranon stress fractures can become chronic, preventing the bone from fully healing and making it difficult to continue sports. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to smooth recovery and return to sports.
Outpatient Reception & Consultation Hours
| Business Hours | 月 | 火 | 水 | 木 | 金 | 土 | 日 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13:00~17:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
| 18:00~20:00 | ● | ● | ー | ● | ● | ー | ● |
【Closed Days】 Wednesday, Saturday, and Public Holidays.
※translates to "Reception ends 30 minutes before the end of consultation hours."
